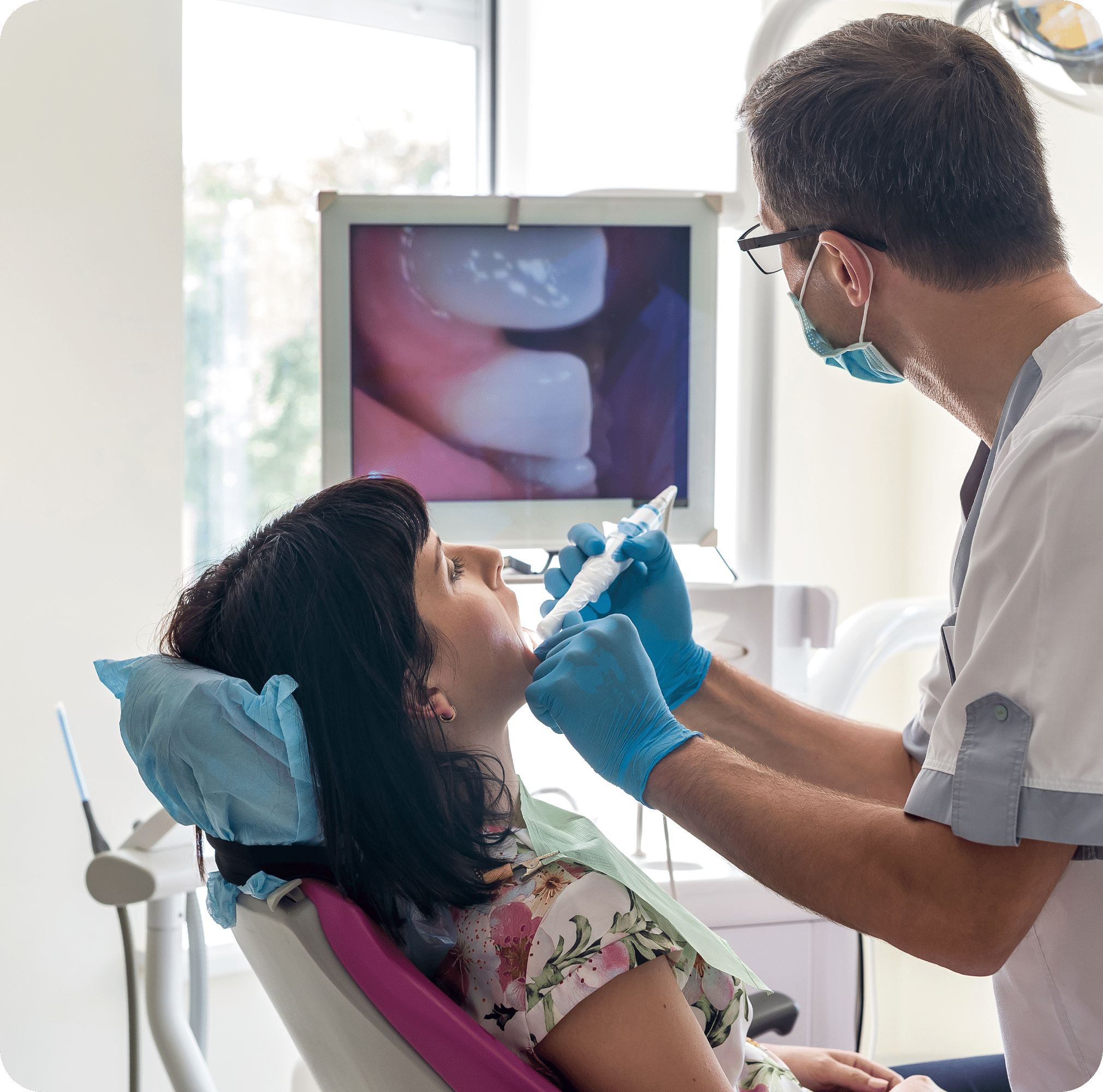

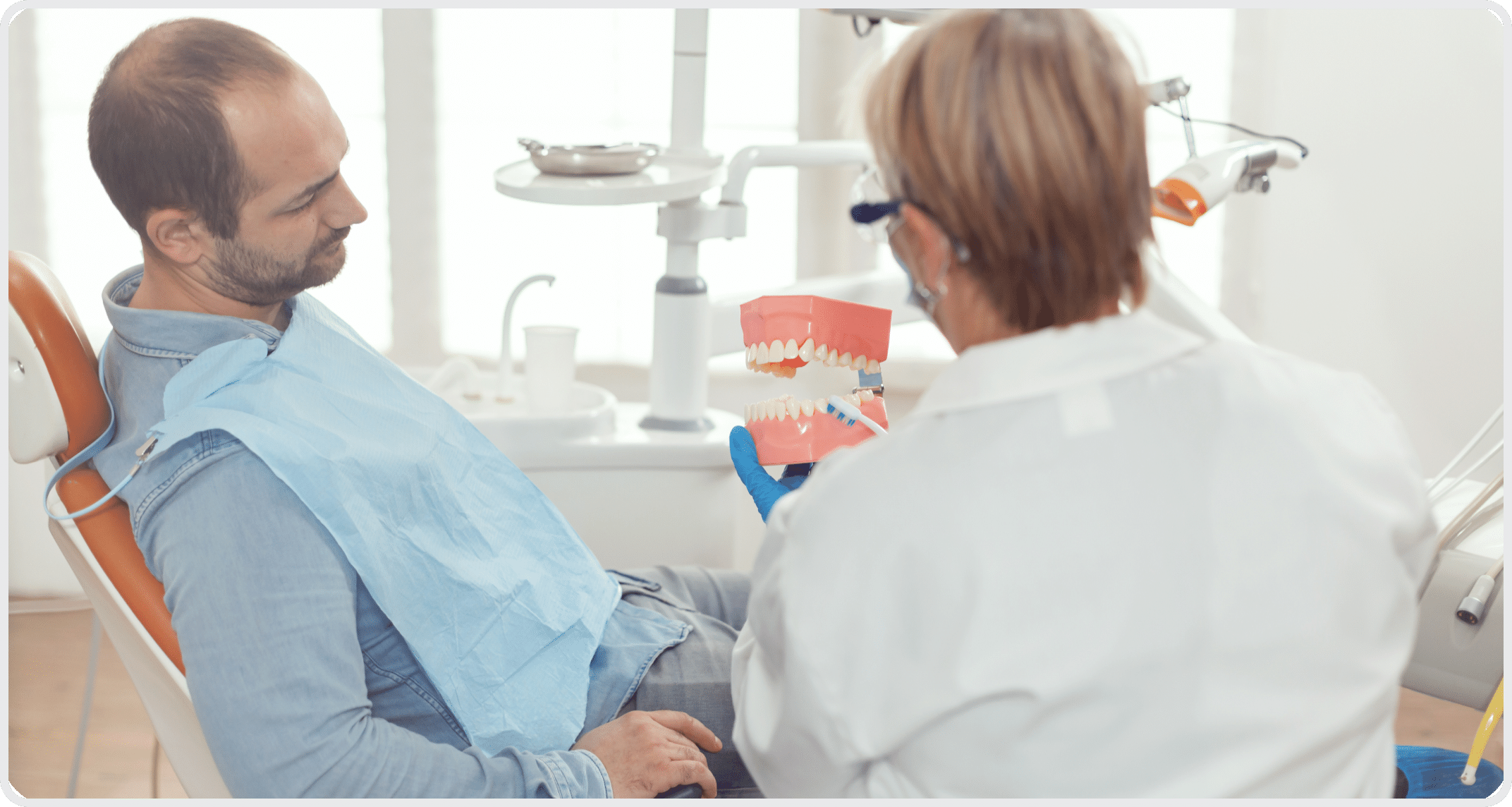
As with any cancer, early detection and diagnosis is critical to survival. It is important for patients to see an oral healthcare professional regularly, particularly if they are considered high risk those who use tobacco, abuse alcohol or have been
exposed to HPV.
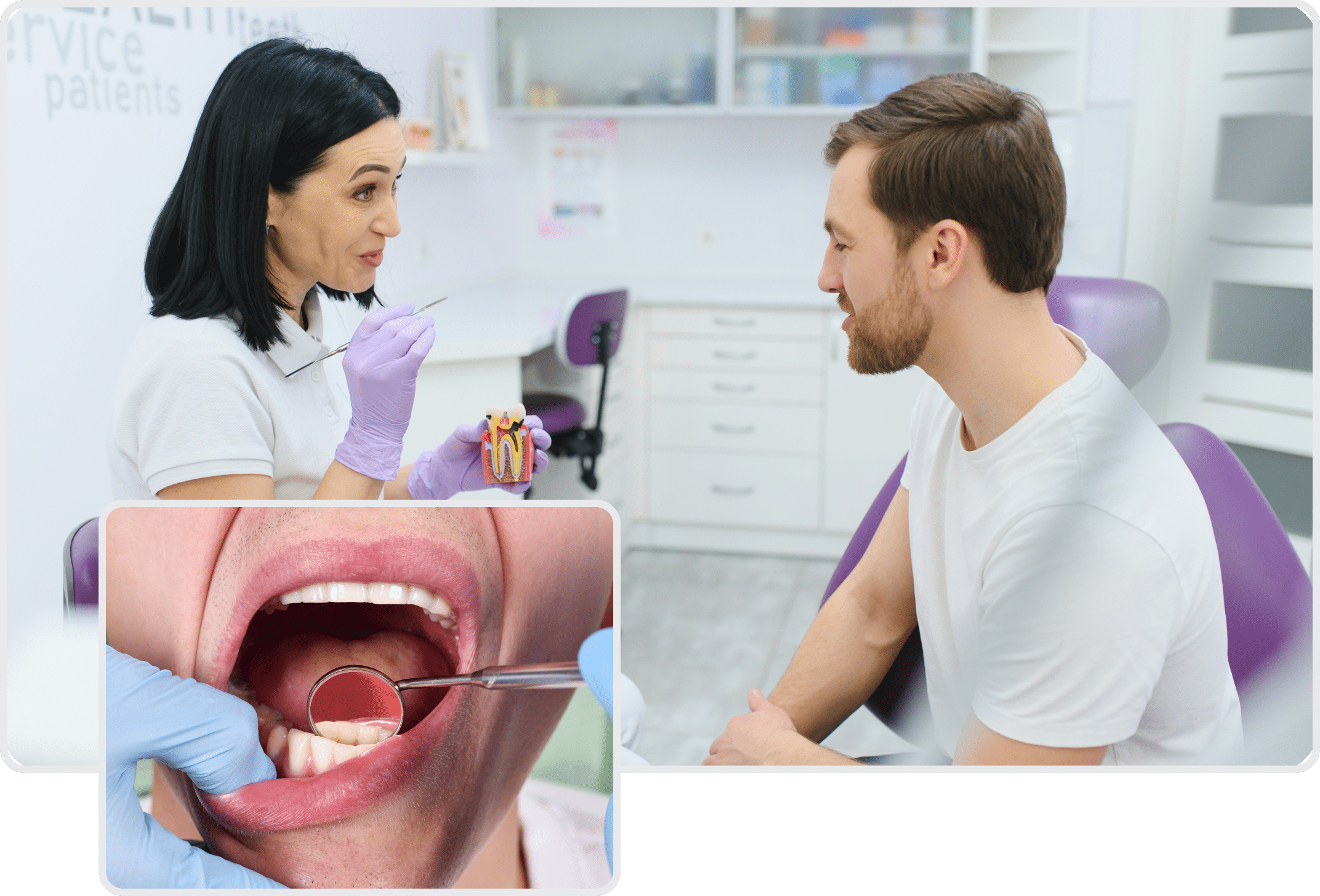


treating oral cancer
1
Like all cancers, oral cancer begins with genetic mutations within the cells of the mouth or throat. These mutations can be caused by various factors, including smoking, chewing tobacco, excessive alcohol consumption, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, sun exposure (in the case of lip cancer), and genetic predisposition.
2
Once the genetic mutations occur, the affected cells begin to grow and divide uncontrollably. This leads to the formation of a mass or tumor within the oral cavity.
3
As the tumor grows, it can invade nearby tissues and structures in the mouth, such as the tongue, gums, palate, or throat. This invasion can cause symptoms such as pain, difficulty swallowing, or changes in speech.
4
In advanced stages, oral cancer cells can break away from the primary tumor and spread to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system or bloodstream. Common sites of metastasis include the lymph nodes in the neck, as well as distant organs such as the lungs, liver, or bones.
5
Symptoms of oral cancer can vary depending on the location and stage of the disease. Common signs include persistent mouth sores, red or white patches in the mouth, unexplained bleeding, numbness or pain in the mouth or lips, difficulty chewing or swallowing, a lump or thickening in the mouth or throat, or changes in voice.
6
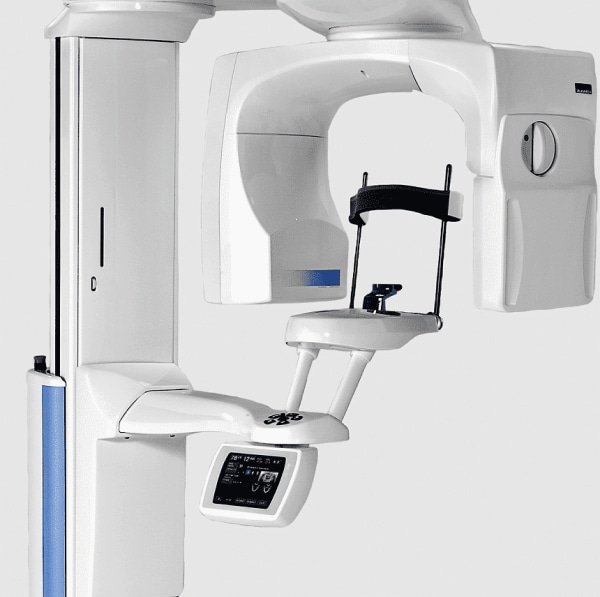
Oral cancer is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and diagnostic tests such as biopsy, imaging studies (like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI), or laboratory tests.
7
Treatment options for oral cancer may include surgery to remove the tumor and affected tissues, radiation therapy to target and destroy cancer cells, chemotherapy to kill cancer cells or stop their growth, targeted therapy to block specific pathways involved in cancer growth, or immunotherapy to boost the body's immune response against cancer cells.
8
The prognosis for oral cancer depends on various factors, including the stage of the disease at diagnosis, the location and size of the tumor, and the individual's overall health. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. After treatment, patients typically require regular follow-up appointments to monitor for recurrence or complications and to provide supportive care.


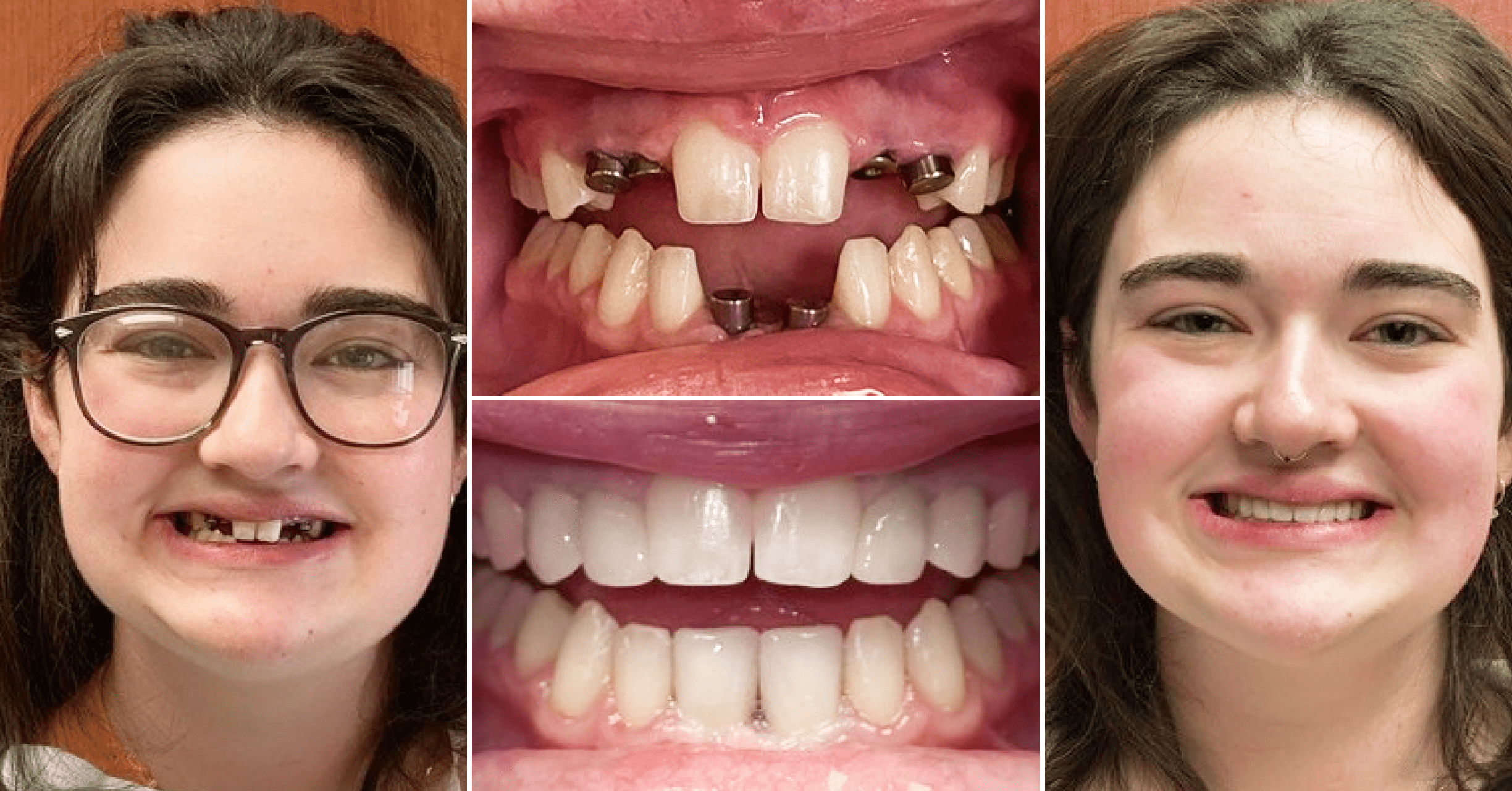
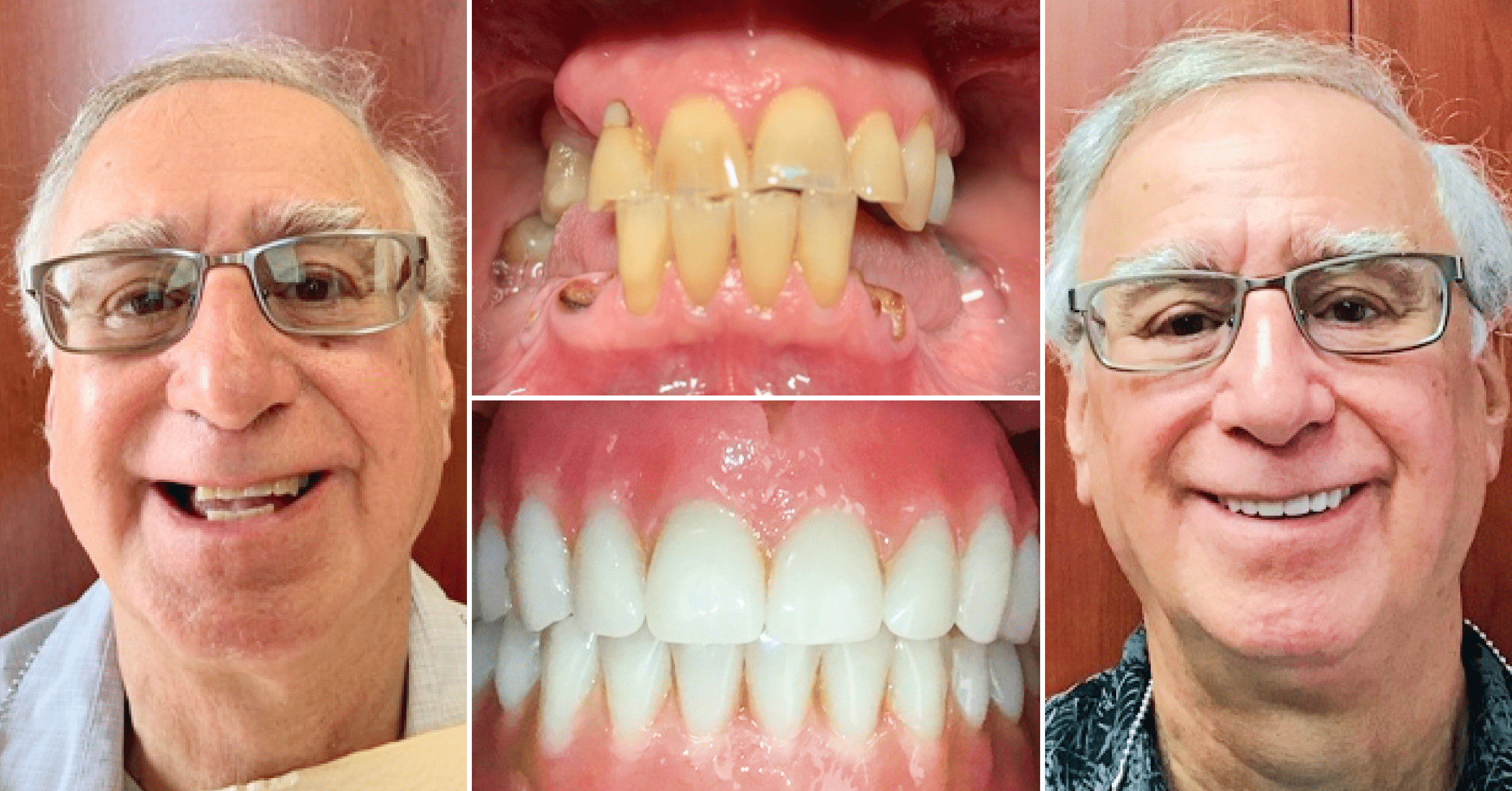
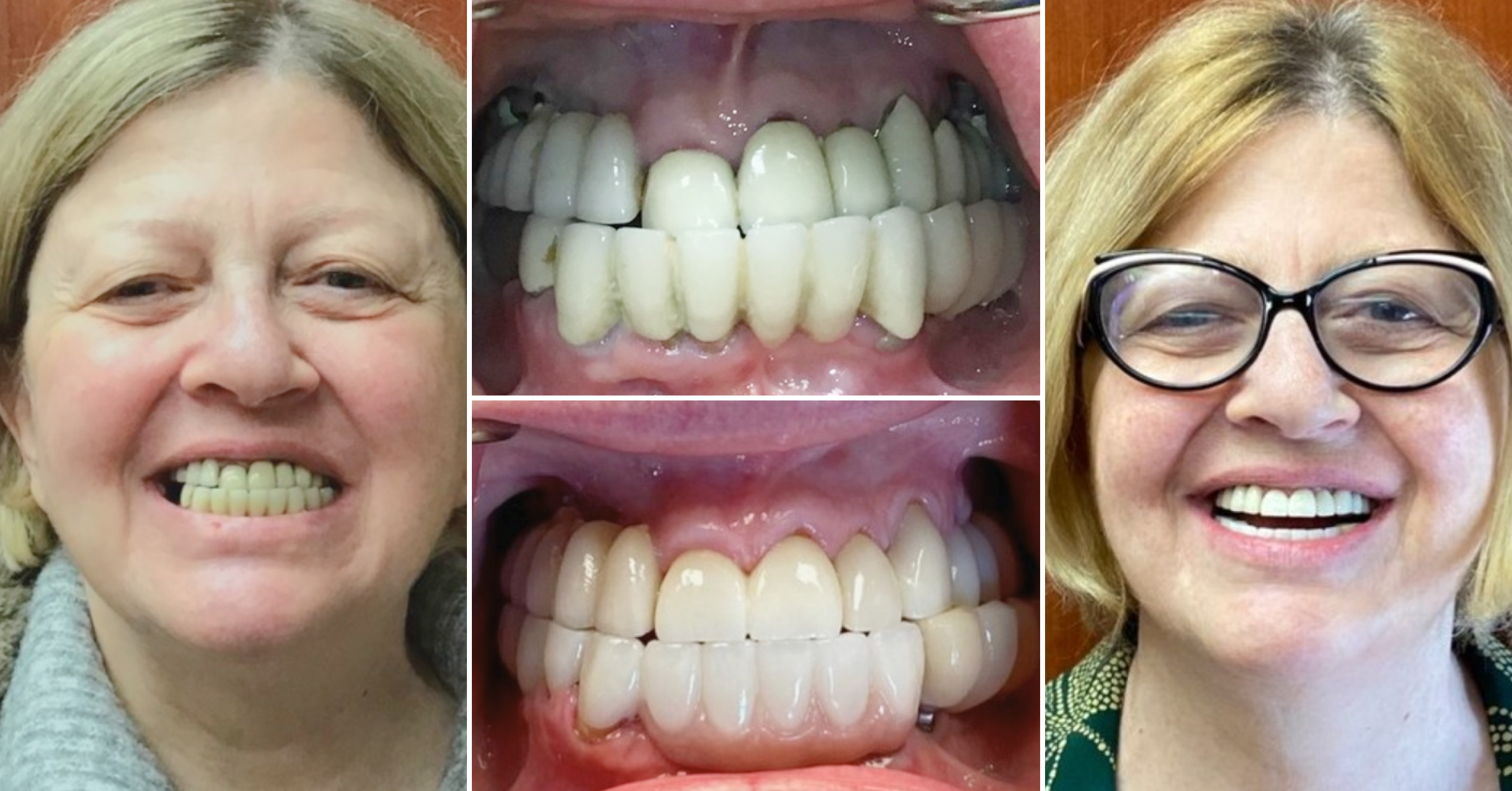
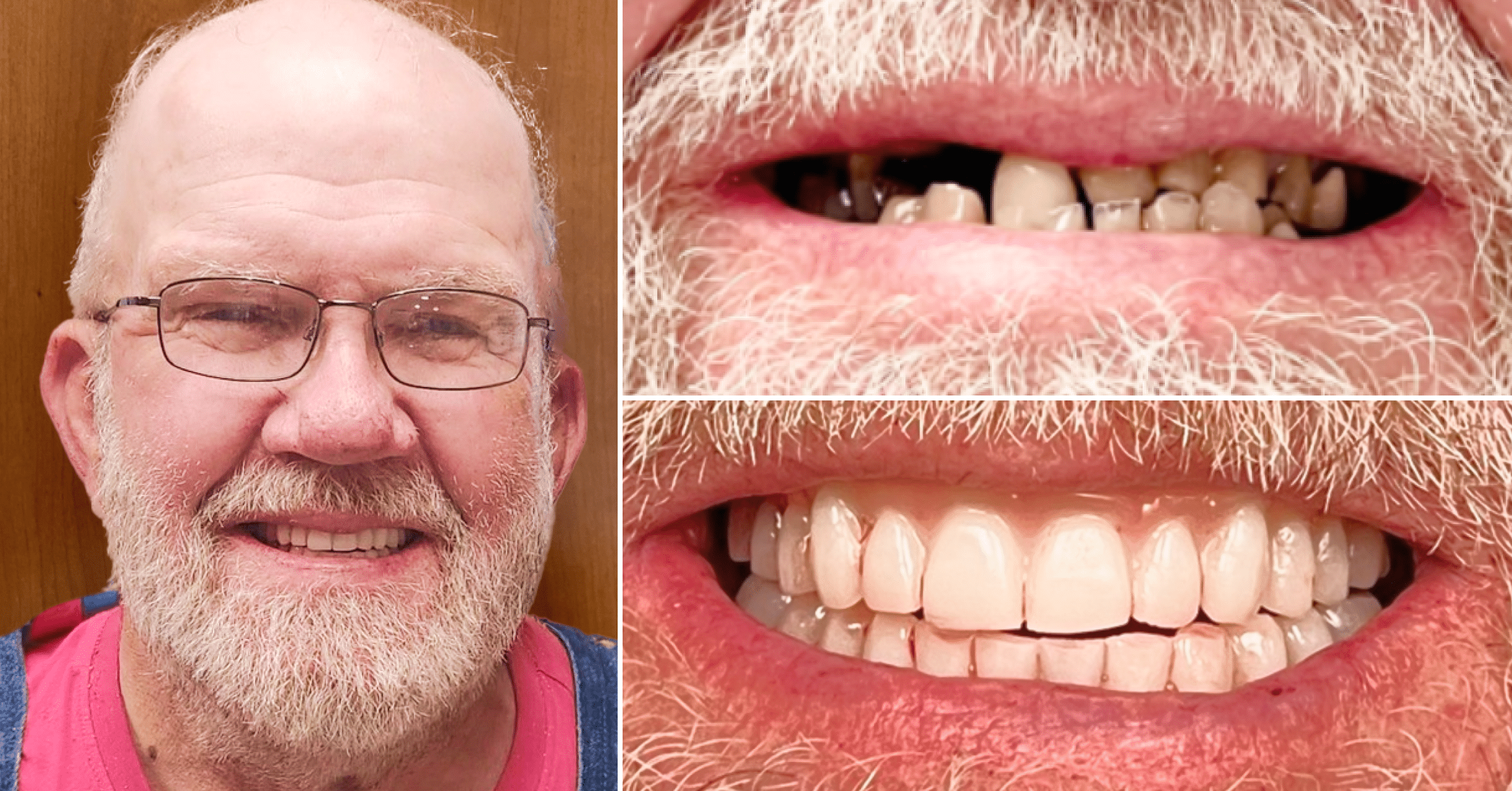
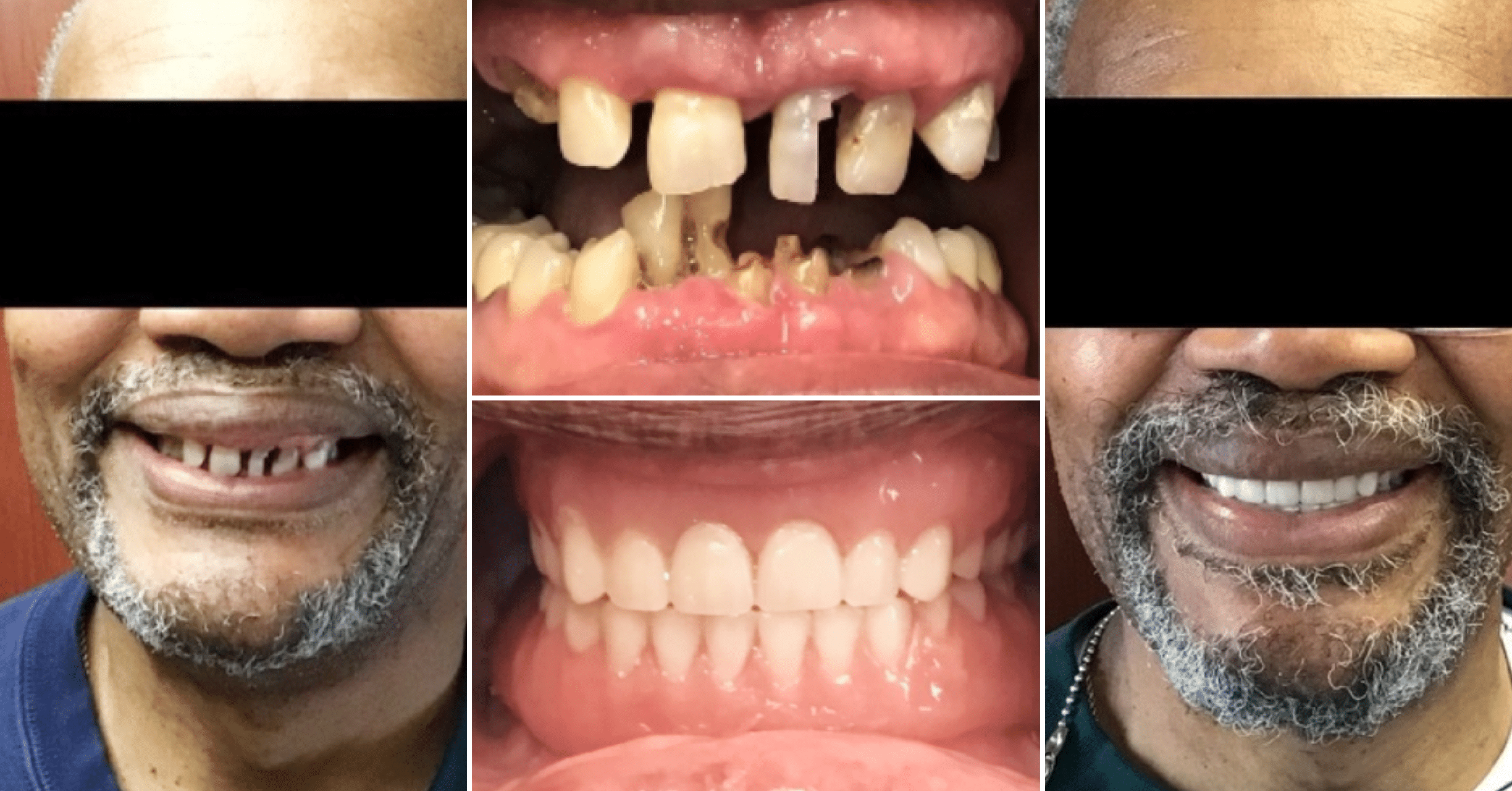
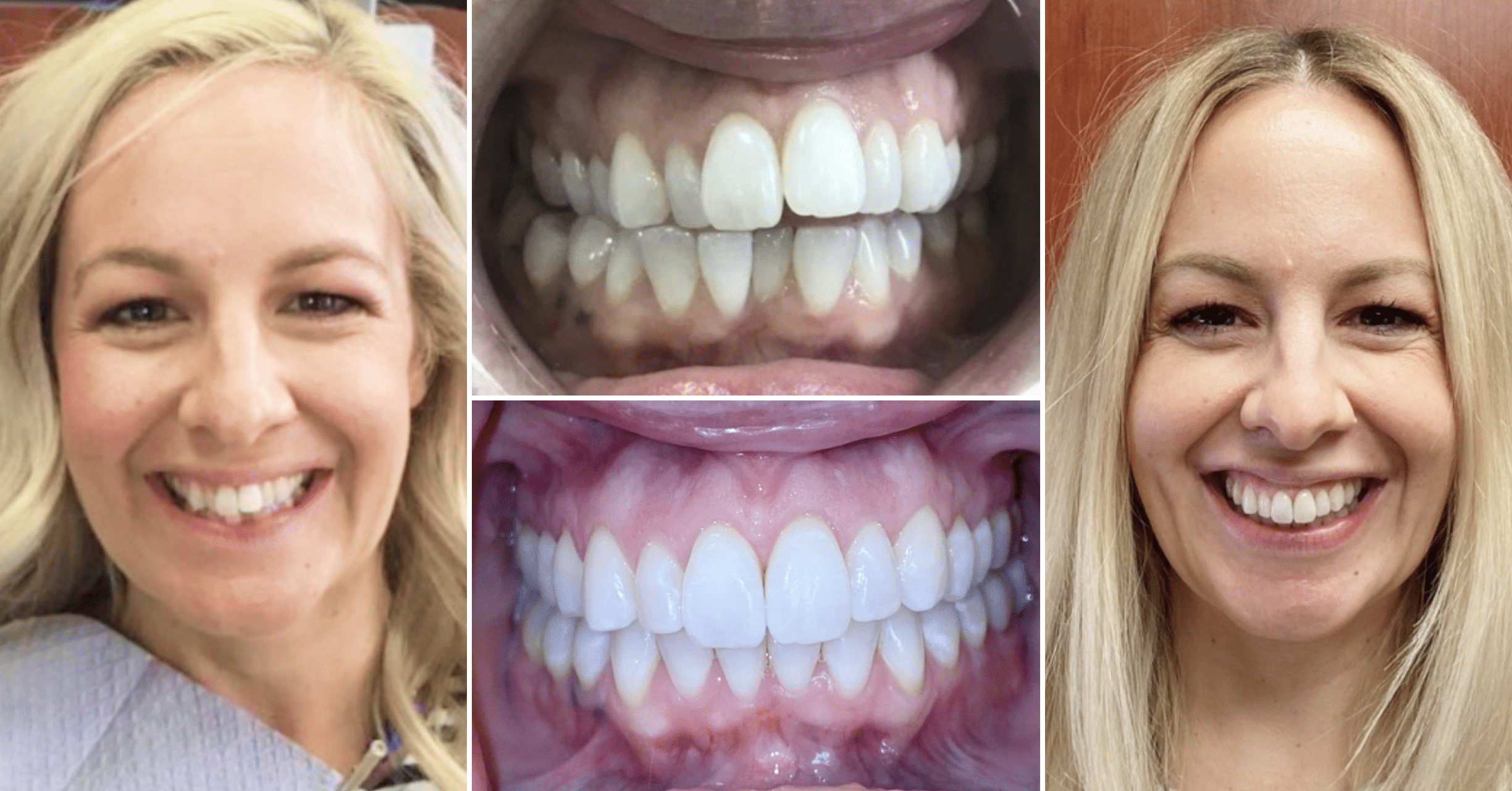
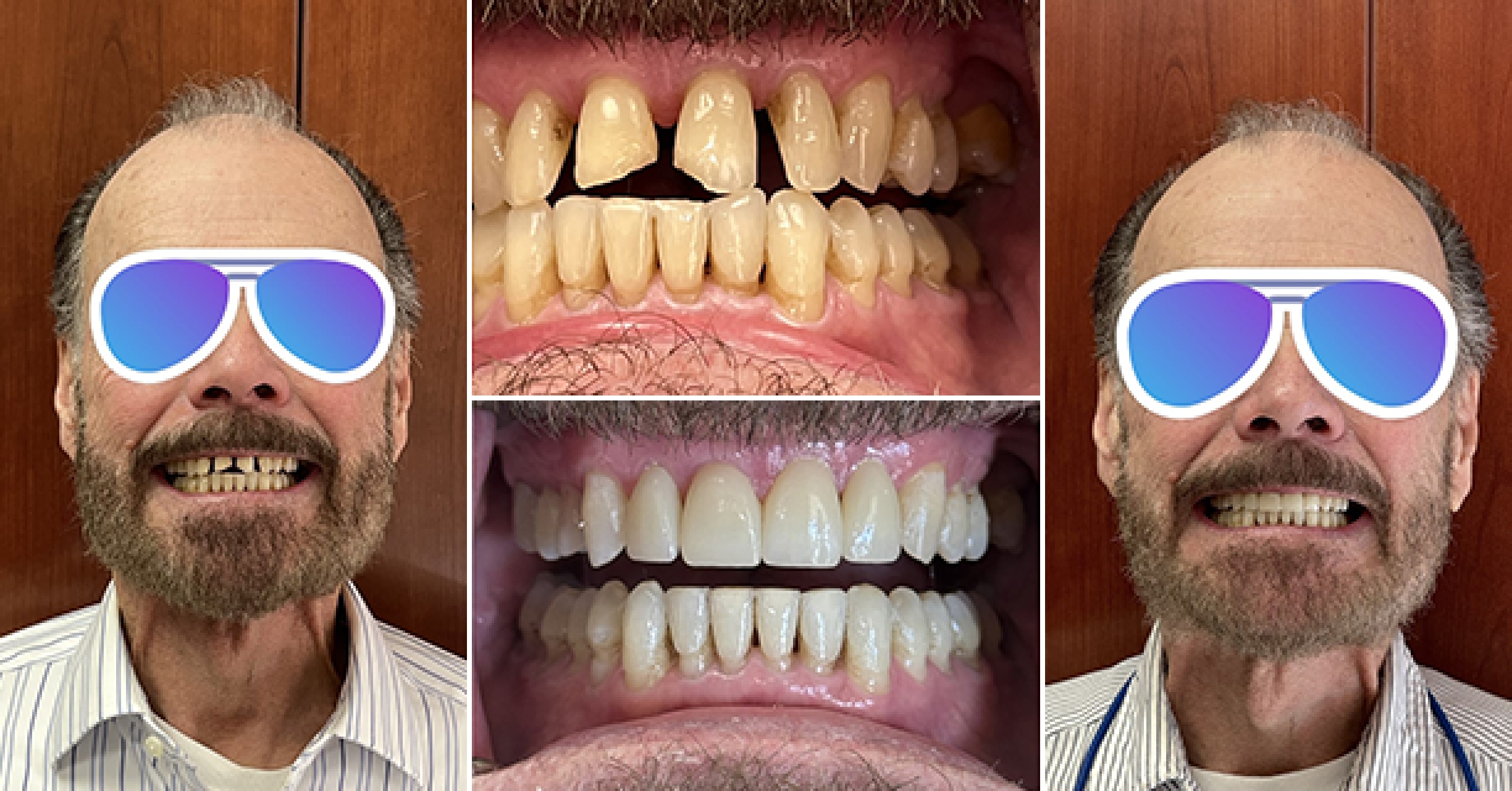
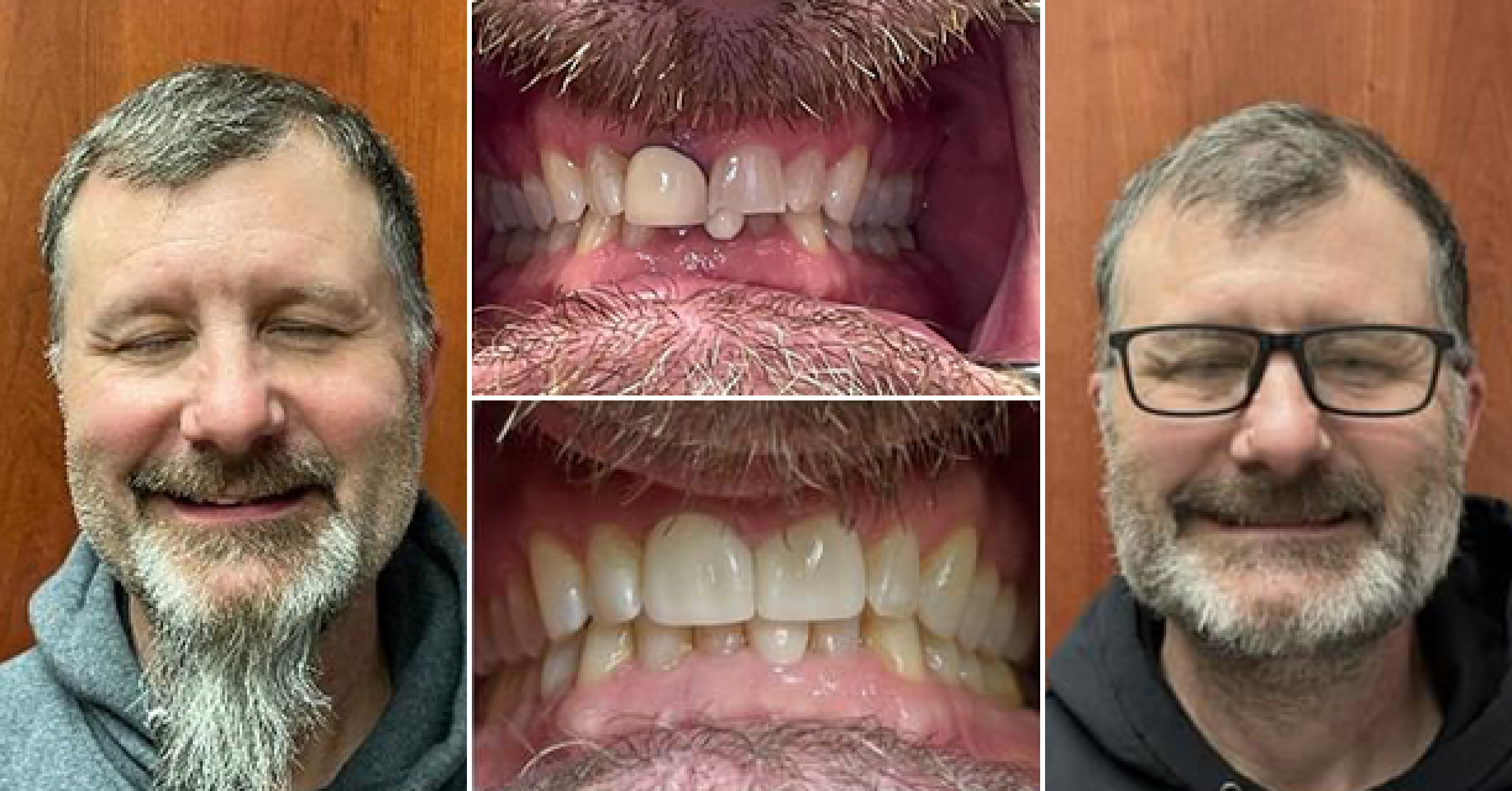
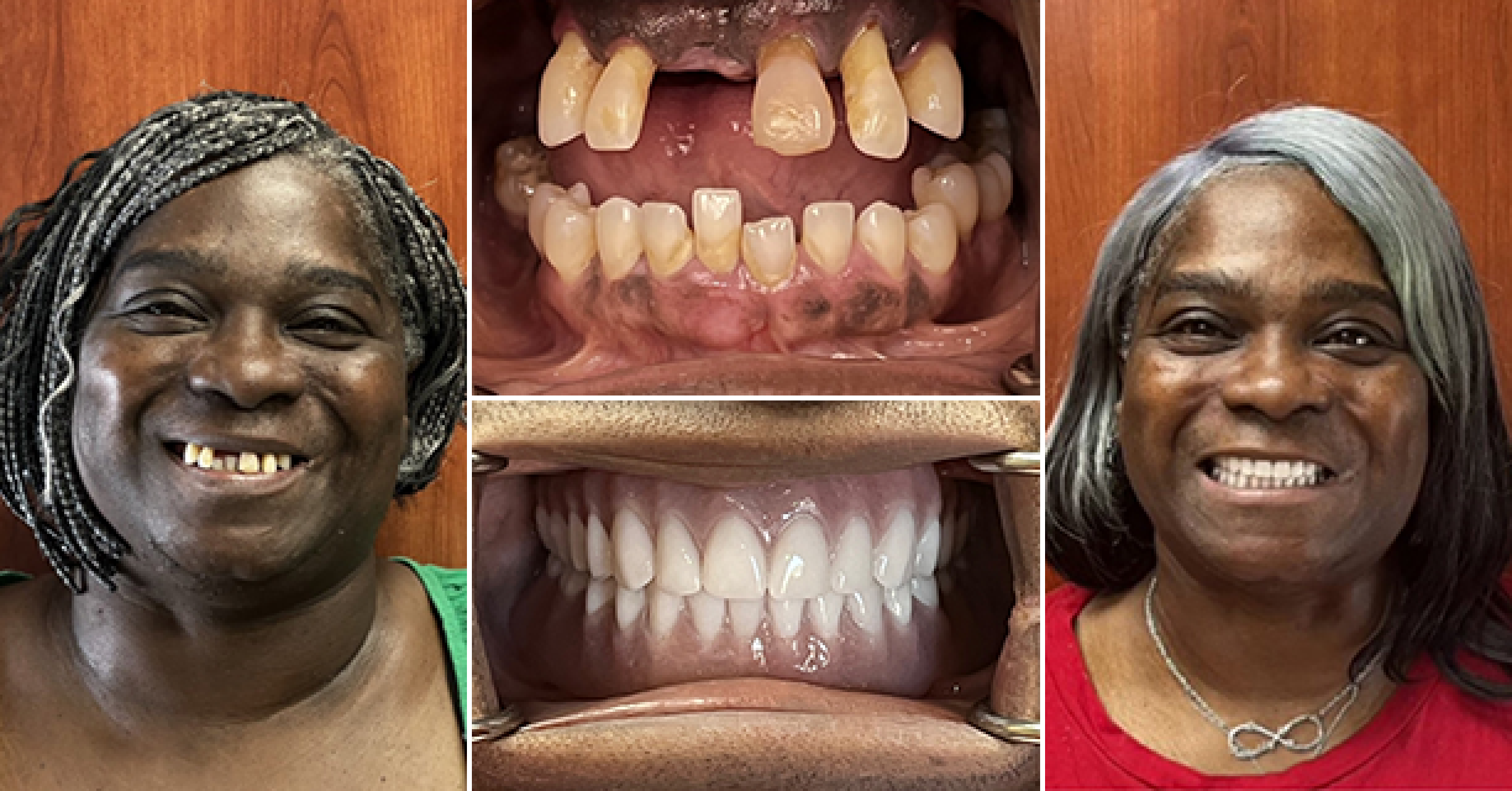
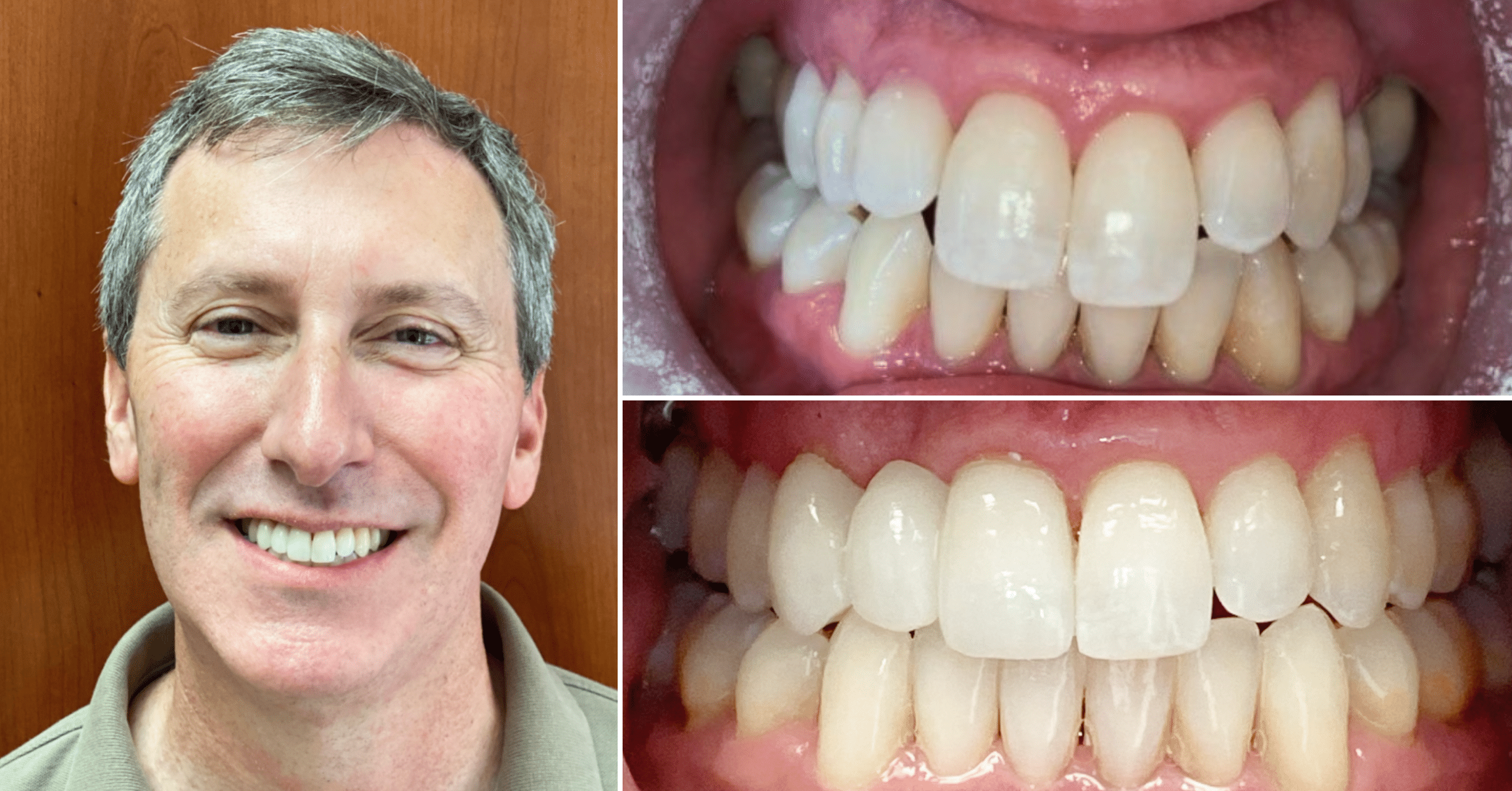









Where we give people a reason to smile. Our team is dedicated to providing Dental Care that works best for your lifestyle.